From Learning to Doing
Many years ago I was teaching high school English on a small island in SE Alaska. I asked the class to compare a piece of literature to the story of the Three Little Pigs. Half of the class couldn't do the assignment because they had never heard of the story of the Three Little Pigs. That changed me forever.

Without shared experiences, learning communities often talk past each other. Inevitably there is a judgement on one side or the other. Each learner brings his/her own experiences to a conversation and uses those unique experiences to make sense of things. Coming together as a learning community to sort through what we understood from something new that is introduced to us is sometimes very frustrating because of all the different experiences brought to the table. To help with that issue in almost any learning community, you can initiate a common experience/action for all participants. When an action is experienced together, suddenly there is more justice in the conversation. The playing field is leveled and the real conversation can begin.

This is a depiction of how that process can be set up for any learning community. The condition is that the learning spiral never ends....every round goes higher, higher. The outcome is that participants almost always feel like they can act on their new knowledge and continue the learning cycle on their own.

Click HERE to access the "From Learning to Doing" resource. A slide presentation on how to create shared experience in a community to initiate actionable change.
Click HERE to access the slide show directly at prezi.com

Cindee Karns, a life-long Alaskan, is a retired middle school teacher with a master's in Experiential Learning. She is founder/weaver of the Anchor Gardens Network, which is attempting to bring increased food security to Anchorage. She and her husband live in and steward Alaska's only Bioshelter
Appreciate Network Weaver's library of free offerings and resources?
Donate below or click here
thank you!
The Angel's Mafia: elements to be addressed in peacebuilding governance
Our Better Angels need to get their act together.
I find myself looking back at five years working in peacebuilding and conflict transformation. Almost as long as I spent working as a mechanical engineer in the aerospace field. The business of designing and building spacecraft has one commonality with the “business” of building peace: they both involve people getting together and doing stuff. I used to be weary of the term peace-building as it implies the linear construction of something which can be described as an emergent property of a complex system. What is peace anyway? No, I’m not going down this rabbit hole now, but I leave the open question here for you to entertain yourself with.
You can’t really build peace the same way you build a Falcon 9 rocket. You can’t build the relationships between people the same way you build a clock but you can create the conditions for relationships to emerge, to strengthen and evolve. You can build the scaffolding that makes peace a more likely outcome than violent conflict. A Falcon 9 is just a very complicated clock. Peace is more like a cloud that emerges out of thin, moist air.
Back to my point: I left my engineering career in pursuit of a revelation. And that revelation has come back to haunt me, five years later.
Whether you’re building rockets or building peace, people have to come together and coordinate efforts to accomplish a Mission.
People have to get themselves organized. If it’s the rocket they’re building, the way of organizing is pretty straight forward. It’s a linear process. We’ve been building rockets for quite some time now and have learned a lot about how to do that efficiently. There are still some hiccups every now and then. When these happen, it’s up to the skills and mastery of the project manager (PM) and systems engineers (SE) to make sure they don’t compromise the Mission. The Mission is sacred. You may be an expert planner but as a PM, you’ll be judged by how creative you are when dealing with the hiccups: a delayed supplier, a volcano eruption, a failed test, a new requirement, a pandemic or a world war. The best PM’s I have met in my previous life were those that knew that you need to be ready to deal with contingencies and uncertainty. This is where a good governance system comes in handy. Running the day to day operation of an engineering team requires discipline, practice, expertise and structure. You’re inside a bubble of control. When this bubble bursts and the outside world comes barging in, you need something different. You’re operating in a different regime. The outside world is complex. Full of interconnections and invisible, mysterious forces. Enter the Law of Requisite Complexity which states that “In order to be efficaciously adaptive, the internal complexity of a system must match the external complexity it confronts.” And this was my revelation back in the day: management is different from governance! Management is all about the plan. Governance is about dealing with situations where the plan that you had is no longer the plan that is needed.
With the exception of perhaps the mafia or terrorist neworks, we don’t know how to organize in an enviroment of complexity and uncertainty. Since we enter kindergarten (and perhaps even earlier through models unconsciously passed on by our parents), we are conditioned to think that someone else, a parent, a teacher, a headmaster, a boss, a political leader, a country, a government, an institution, an NGO, you name it, must have The Answer. someone must have The Plan. Someone must have An Understanding of what is going on. Someone will manage it!
When faced with problems that, by definition, have no well defined problem-statement, no boundaries, no solution, we revert to this very rudimentary, almost medieval governance system where a few (typically old, white) men call the shots for all of us. I have nothing against old experienced men calling the shots sometimes (they may have some clever ideas), but I am against this being the only form of social organization in complex environments.
The peacebuilding world has taught me a lot about what it takes to thrive in a complex and ambiguous environment. If you survived a civil war and are engaged in local peacebuilding, you’re pretty much an expert in the Vuca World. I struggled to find my voice in this field. After all, what do I know about peace? I have never heard an AK47 fire.
I found my voice in the overarching theme of social organization and governance. When complexity and uncertainty (aka real life) bursts through your control bubble, that’s when investing in a governance system that obeys the law of requisite complexity makes it or breaks it. After five years witnessing the efforts of 24 South Sudanese Angels coming together for peace, here are a few elements I believe should be addressed when thinking about governance systems.
Communication, language and meetings
Communication is the essence of human social organization. For better and for worse, we’re doomed to use language to communicate and coordinate with one another. The pandemic zoom years have shown us that, while it is possible to keep in touch and even do management decisions remotely, there are times when a face to face meeting is unreplaceable. Whoever feels like a peloton bike is a full replacement of a regular bike has probably never experienced the bliss of a bike ride by the beach in a warm, spring morning.There are moments in the life of a peacebuilder when you literally need to see eye to eye. Feel the energy in the room, let your body speak and listen. There’s simply no virtual replacement for this. The same holds true for any team. There’s simply no replacement for a well facilitated face to face meeting when what’s at stake is the future of the Mission.
Non-violent communication, skillful facilitation of meetings, hosting space for convening, trust building and sharing, are all necessary groundworks for building a solid governance system. The groundwork needs to be in place and ritualized before going into the hard and messy part.
Sense-making, meaning-making, decision-making (SMDm)
What just happened?
If you’re convening a governance meeting, chances are, something happened. Because everyone on the team is so focused on his or her own subsystem, trying to draw a complete picture may be challenging. Typically, we jump too fast to conclusions here. This is where systems thinking comes into play. Every person in the room will contribute with his / her own perspective on the system and so it’s really important to facilitate a sense-making session that casts a wider, systemic lens on the issue. Whatever happened is the result of a system. Whether you’re aware of it or not, it’s 100% guaranteed that there’s an underlying system moving the pieces. The aim of this sense-making session is to flesh out the elements of this system and move to the next phase of the discussion by asking “What does this mean for the Mission?”
For the engineer working on Falcon 9, it’s relatively straightforward to answer this question. It may take some research, modeling and forecasting but it should be possible to figure out what a delay in the delivery of a component means for the whole mission. Remember, it’s just a very complicated clock, not a cloud.
This is not the case for peacebuilding. The meaning of whatever just happened is deeply related to your own individual meaning making structures and how it is shared with the collective. Collective meaning making in social complex systems is impossible to do without some agreement of what reality is. Without this agreement (or “epistemic commons” if you will) how do we know what we know about the social reality and how do we co-create a shared social imaginary? You need to have a shared dream or shared goal to work towards. Without this shared dreamland, collective meaning making becomes impossible.
If sense and meaning are shared (easier said than done), proposition crafting and refinement should easily flow out of the previous steps. What?, So What?, Now What? This is the way many Western philanthropies and organizations talk about learning and adapting “and governance” itself is a very Western word with all sorts of unintended connotations. However, this is a universal human concept. Every culture has a way of making decisions. We in the Global North tend to sometimes forget that every day all over the world, people in communities come together to come up with proposals to solve problems. Working in smaller teams or networks could prove to be extremely creative and effective if it is coupled with a decision making process, such as consent decision making to fast track good ideas into actionable prototypes and have a basic foundation for what to do when you do not agree or the plan goes sideways.
Finally, the governance process should answer two cornerstone questions: accountability and legitimacy. Whatever comes out of the process must be accompanied by a clear statement of accountability (who has skin in the game?) and legitimacy. In Western contexts, charters, MoU, constitutions, manuals, contracts, can play a role here. But these can overcomplicate the real work. What I have found in my time in peacebuilding is that the deepening of relationships and agreement for action can start with three questions. What do we want to do together? How will we make decisions? What do we do when we don’t agree? In short, how do we want to show up together? This is one area where I think there’s a lot to innovate in civil society movements. Peacebuilders can learn from movement activists how to set the foundation for adapting quickly while keeping a focus on the desired goal.
Organizing for Peace
Kurt Vonnegut knew it: “There is no reason why good cannot triumph as often as evil. The triumph of anything is a matter of organization. If there are such things as angels, I hope that they are organized along the lines of the Mafia.”
I believe that our perennial mission is to organize. We do that so elegantly with clock problems. Now it’s time to complement that toolset with other rituals that help us organize around cloud problems, too. I hope Pinker’s Better Angels take a lesson or two from the Mafia, but outrage or hope alone won’t cut it. I believe there’s a lot to be done to help peacebuilders around the world get organized in a way which creates, not a rigid, but an emergent order that is able to sense and respond to the challenges posed by the destructive forces of violence and war.
Pedro Portela is the Founder of the Hivemind Institute, a think tank and action research organization in Portugal dedicated exclusively to prototype new models of local organization, advocating for more systems literacy and proposing networked approaches to complex social problems.
Originally published at The HiveMind
featured image found HERE
Appreciate Network Weaver's library of free offerings and resources?
Donate below or click here
thank you!
MAKING LARGE EVENTS PARTICIPATORY
This blog was originally published in October, 2019, when we couldn’t foresee that most large events would cease. As we anticipate meeting again in person, I hope the approaches here give you ideas. You might like to check out my new meeting design coaching services.
It’s possible to make large events participatory and interactive. Here we share our latest inspiration and approaches, from recent work with events from 50 people to over 200 people. The topics and audiences vary, yet the desire to inspire and connect people, enhance learning, build connections, and advance work beyond the meeting is the same. Here’s what goes into our secret sauce for creating a participatory, inspiring event:
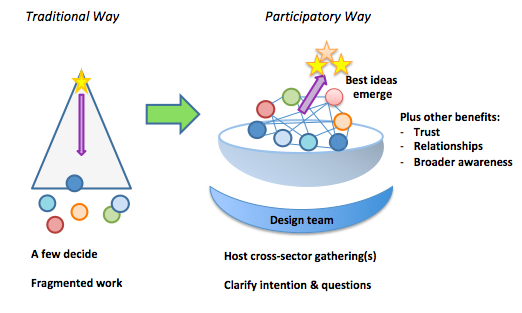
Participation starts in design: Working with a design team that includes representatives of the people who will be participating in the event helps ensure the event format is relevant and effective. This group can:
- Bring varied perspectives to clarify the context and conversations that are needed now. For example, with a state-wide food network that’s been underway for five years, we landed on this strategic question: How can the structure and approaches of the network galvanize and support action and momentum at the local, regional, and state levels? It took some thinking and conversation to get clear that this was the most powerful question for this moment. We brought in case studies to spark the conversations.
- Provide input on the format of the meeting and who to invite and how, e.g., you can access the broader social and professional networks of those in the room to learn about other people, organizations, and initiatives who could be invited.
- Serve as ambassadors for the vision and the meeting/initiative, spreading the word, helping with invitations, and sharing feedback they are hearing.
For example, we co-facilitated the annual meeting of the Greater Nashua Public Health Network, with a focus on building a trauma-informed community. The design team helped us get a sense of how much training had been done so we could tailor the content of the training portions. We agreed on a clear set of desired outcomes and went through several rounds of an agenda design, tailoring and improving it each time, based on their feedback.
At the event, start with stories: Getting people sharing stories early in the day builds relationships and creates a warm, welcoming environment. Our approach is inspired by an exercise called Radical Acceptance, which I learned from taking improv classes with Boynton Improv Education in Portsmouth, NH. This simple exercise builds a sense of emotional safety and encouragement for everyone to speak up. I modified it slightly by doing the following:
- At round tables, invite each person to introduce themselves and share one brief story of something going well in their work. Invite everyone to respond with a “yes!” or any other enthusiastic positive response. Then the next person goes and the group does the same. Across the room you hear “yes!” and clapping and laughter, and see fist bumps.
- In another variation at the Nashua meeting, we asked each person to share one thing they appreciate about Nashua/the region and put it on a post it note. We used the same process I mentioned and then collected these and had a graphic facilitator make a poster of the themes.
This only takes 10-15 minutes. Sometimes people pick up on the “yes!” and bring that positive response into other parts of the day, often with a shared laugh.
Offer inspiration/new ideas and new voices: Beyond the standard keynote presentations and skill-building workshops, consider having shorter TED-talk type or PechaKucha presentations (presenter has about 7 minutes to talk with 20 image slides) and featuring voices beyond “experts,” e.g., youth, those with lived experience, people from marginalized identities or communities.
Host cross-pollinating small group conversations: The World Café process taps the ideas of everyone in the room and allows people to make new connections and learn from each other. At an anti-racism gathering of 200+ people from Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont, we invited people to talk in a group of four with people from their state about what is working in anti-racism work. In the second round, they mixed to a new group of four with people from other states, sharing themes from the previous conversation, and then talking about what more was needed. With 200 people, this meant we had 50 four-person conversations each round (100 total), which is a lot of learning and information exchange…and fertile ground for new relationships and collaborations to form.
Allow space for self-organized deeper dive conversations: All of the conversations and ideas percolating through the first part of an event can be given a space to land and deepen if you design space for that. Inspired by the process of Open Space, here’s an example of how we organized this at the event with 200 people:
- During the morning sessions, we asked people to submit topics they’d like to discuss with others at an Open Space/deeper dive conversation session that afternoon.
- Over lunch, we grouped these into about 16 overall topics. I made folded table tents with a table number and name of the topic and put these out on the round tables. I sketched a chart showing table numbers and topics, took a photo, and put it up on a slide.
- When that session began, I invited people to join the topic they’d like to discuss and walked around with a roving microphone to introduce the topics and show which table was where, with the slide image as another guide.
- We asked for a note-taker at each table. For topics where lots of people showed up, we invited them to split into several tables. At the end, we heard brief highlights from the table conversations.
At another event, we had time for people to rotate to a second topic table, while some people stayed at the first one, building in another layer of connection and cross-pollinating.
The range of topics that were suggested were far beyond what our design team would have thought of, and we learned which areas had the most interest. People had the freedom to initiate or join conversations and connect with others with similar ideas, concerns, and questions.
I wish I could somehow visualize and learn all the seeds that got planted at these events. We offered the fertile ground – so time will tell what grows!
Beth Tener is a leadership trainer and coach who helps social change leaders live their values as they address complex challenges, such as transitioning to a clean energy economy, disrupting racism, and revitalizing communities. She is passionate about bringing people together in ways that unlock and ignite personal, group, and community potential. She is the founder of New Directions Collaborative, based in Portsmouth, NH, and has worked with over 200 organizations and collaborative networks.
originally published at New Directive Collaborative
featured image found here
Adapting a network’s theory of change
Collective Mind hosts regular Community Conversations with our global learning community. These sessions create space for network professionals to connect, share experiences, and cultivate solutions to common problems experienced by networks.
On September 22nd, 2021 we met with Carri Munn from Context for Action and Amelia Pape from Converge for our first Community Conversation of the fall. Carri and Amelia shared their experiences collaborating with network teams to adapt Converge’s theory of change to their networks and the process and successes of co-creating a shared theory of change with network leaders.

Highlights from the conversation
Complex problems are by nature nonlinear and typically must be addressed from many angles at once. This is why networks, in their ability to connect and facilitate collective action between people and organizations, can be successful and impactful in creating system change in complex environments. As defined by our co-hosts, a theory of change describes how a network can create systemic change by harnessing the interdependence of the network system – its members.
The way networks create system change – or their theory of change — can often emerge in phases. The conversation outlined these phases, beginning with connecting the actors within the network system, working towards building trusting relationships and an understanding of members’ contexts. This is the foundation necessary to reach the coordination phase, when regular communication and coordination starts to occur between people within the network, people are supporting the work and each other, silos are starting to break down, and information, value, and learnings begin to flow from the connections that have been created. From here, the collaboration phase emerges and members begin to recognize a shared purpose within the larger system and opportunities to collaborate within it. It is these emergent collaborations that begin to create and perpetuate more and new collaborations and, eventually, system change and impact at scale.
This phased framework is a way to talk broadly about a network’s theory of change. However, network leaders often need a specific and contextual theory of change to effectively communicate to and strengthen the network. Our co-hosts shared an example of using this framework to support a network interested in transforming a broad theory of change to one that represented their network’s specific activities, as a means to communicate and collaborate more effectively with its members and stakeholders.
Using the phased theory of change framework — connection, coordination, and collaboration — our co-hosts described their process, which started with using surveys and conversations to gather information from the network about the challenges, barriers, and opportunities that existed within the network system in its current state, and to describe the optimal system impact, or the realized vision, they hoped to achieve. These became inputs for a virtual Mural storyboard session where they facilitated a smaller group of network participants to articulate what they hoped to create and achieve in each phase and how they viewed their roles and relationships within these phases. The storyboarding exercise was a way to help the network articulate how they would create the conditions for impact and collaboration to emerge that would be considered those of a healthy network and then use those outcomes as a tool to communicate with and bond the network.
What also emerged from this conversation was the critical role of network coordinators in theory of change processes. Coordinators are often the catalyst in orienting networks to see the bigger picture. As facilitators of a complex system, it often falls to them both, by necessity and design, to engage members in conversations about how they see themselves as part of a larger whole and how to contribute to transformational change in the network system.
Miss the session? View the recording here.
Sign up for the Collective Mind newsletter to receive these in your inbox!
Thanks again to our co-hosts, Carri Munn and Amelia Pape!
Get involved
Have your own experiences developing a theory of change? Tell us about it in the comments below.
Join us for the next Community Conversation!
Or email Seema at seema@collectivemindglobal.org to co-host an upcoming session with us.
original article published HERE
Experimenting Towards Liberated Governance
Over a year ago, Vu Le published an article about the current models for nonprofit boards. The title “The default nonprofit board model is archaic and toxic; let’s try some new models” doesn’t bury the lede. Of the current models, Le writes:
“Over the years, we have developed a learned helplessness, thinking that this model is the only one we have. So we put up with it, grumbling to our colleagues and working to mitigate our challenges, for instance figuring out ways to bring good board members on to neutralize bad ones or having more trainings or meetings to increase ‘board engagement.’”
At Change Elemental, we have been experimenting with some new governance models, informed by the work of our clients, partners, and many others in the field who are trying out new structures and ways of governing. For example, Vanessa LeBourdais at DreamRider Productions has shared principles and practices of “evolutionary governance”, and Tracy Kunkler at Circle Forward has supported our learning about consent-based decision making. Countless other groups who have continued to uphold and practice historic, ancestral, Indigenous, and intergenerational structures of governance—and have informed these other values-aligned governance models—have catalyzed our learning.
Here, we offer a specific window on the evolution of our board, including some practices we’ve dreamed up, borrowed, and re-remembered to align governance with our values in a nonprofit system set up to default to white supremacy, paternalism, power over, and other oppressive habits.
The following questions have formed the basis of our governance and leadership evolution (we’ve shared more about our leadership evolution in recent blog posts here and here):
- How might we realize deep equity and liberation in leadership and governance?
- How might we evolve leadership and governance structures to share power and work in more networked ways?
- How might we align leadership and governance practices and culture with our values?
Our journey began a few years ago when our board and core staff team began to get curious about what it might look like to think about our board as mycelium. Mycelium are fungal networks that spread across great distances within soil (and sometimes underwater) and process nutrients from the environment to catalyze plant growth, supporting ecosystems to thrive. In our context, we use mycelium to refer to the powerful network of tendrils and roots that connect our board and core team to other people, groups, and organizations, enabling us to turn toxins into nutrients and nourish ourselves through our relationships to ensure collective thriving and care.
Here is what we’ve learned so far in our governance evolution (from the core team perspective—more from our governance team coming soon!):
Shifting language from “board” to “governance team” helped us reframe the governance team’s role.
Early on we shifted from referring to our board as “a board of directors” to a “governance team.” Tracy Kunkler of Circle Forward offered this definition in a small group experiment on governance we facilitated:
“Every culture (in a family, a business, etc.) produces governance — the processes of interaction and decision-making and the systems by which decisions are implemented. Governance is how we set up systems to live our values, and leads to the creation, reinforcement, or reproduction of social norms and institutions. Governance systems give form to the culture’s power relationships. It becomes the rules for who makes the rules and how.”
Shifting language supported us to shift our mindsets about governance. This language guided us towards greater clarity about our own governance team’s role: co-creating systems and practices that can support and catalyze us to live our values. It also deeply shifted how we both hold and reimagine the boundaries between the 12 people on our governance team, our core team (staff), and other partners to be more porous and center collaboration, emergence, and our interconnectedness.
However, because shifting mindsets requires shifting patterns and practice, this switch in language isn’t simple. We have noticed that we sometimes revert to using the term “board” rather than “governance team” when we are talking about potential barriers that the board may present or “traditional” board responsibilities such as fiduciary oversight. This is a work in progress and when we find ourselves reverting to old language, it is a signal that we might be in older practices, patterns, or ways of thinking about our relationship to the governance team and its role that are no longer serving us or our work.
Practicing liberatory governance is having one foot on land and one in the sea.
Getting clearer on our governance team’s role deepened our sense of what it might look like to realize deep equity and liberation in governance. We began to understand what “liberatory governance” could look like for us—a governance team that partners with us to bridge between current reality and the future we’re building by: moving the organization towards greater alignment with our values; and co-creating liberatory systems and ways of working together that can transform the larger oppressive systems we’re operating within. We talk about this internally as “having one foot on land and one on water,” a metaphor Hub member Elissa Sloan Perry shared from Alexis Pauline Gumbs. Gumbs hears best with “one foot in the water, one foot in the sand.”
In our organizational context, the “water foot” attends to things like our vision, uninhibited aspirations, values alignment, and acting today in ways that prefigure the world we want to see. The “foot on land” takes into account the world as it is, such as the requirements and legal constraints of our 501.c.3 tax designation, and current financial realities and access to other resources, where trust-based relationships can sometimes become transactional or even litigious. Our governance model values both “feet” in its awareness and decision-making. When we make decisions, the “water foot” leads with the “land foot” as a valued, supporting, and crucial partner.
Creating multiple, fluid points of connection across the staff and governance team helps build the relationships and trust necessary for shared leadership and power.
Building trust and mutual accountability are at the heart of our evolving governance structures and practices, just as we have found it to be in building toward shared power and leadership at the staff level. This work is more time-consuming than conventional governance models so we needed to build our collective capacity for sensing what is actually too much time. We also needed to strengthen our skill and capacity for generative conflict including discerning when to: enter into conflict and tension; sit with it so that we can reflect and discuss later; and/or intentionally let it go. This has meant getting more comfortable with sitting in discomfort when conflict can’t (or shouldn’t) be resolved immediately.
Some simple structures and systems support us in developing these capacities and discerning what is needed to build trust and move through conflict. For example, we wanted more interaction between our core team (staff) and the governance team, but didn’t want to necessarily add more large group meetings—we wanted connections to be deep and purposeful. To create purposeful connections, where a broad range of staff and governance team members could develop relationships and bring their unique gifts, we opted to have governance team co-chairs work with a staff liaison. The staff liaison partners with different staff, bringing different people into conversations with the co-chairs and other governance team members where their experience, wisdom, and gifts are critical. The co-chairs and other governance team members then connect together and separately into different areas of work based on their interests, skills, and what is needed.
We also evolved our governance team meeting structure to have staff members join for key sections of the meeting. We share the agenda in advance and offer some guidance to help staff decide when they might join or when they might opt out of a meeting. Additionally, staff and governance team members now caucus separately at the end of each governance team meeting to debrief and raise unresolved issues with the intention of sharing back what needs the full group’s attention. The caucuses support greater truth-telling across the governance team and core team, deepen our understanding of each other’s perspectives and help us dig into conflict with love and rigor.
Grounding in shared values is critical for practicing liberatory governance.
If you were to review the specifics of our governance team’s role, you might not find anything surprising or “new.” The difference is in how the governance team carries out these responsibilities – with a rooting in shared values with staff and commitment to working through differences in values when they show up.
In recruiting and engaging governance team members, we haven’t just sought out individuals who conceptually agree with our values (which were reflected in our recruitment criteria), but people who are game to experiment on what it looks like to make decisions rooted in those values. People who already embrace and practice inner work, multiple ways of knowing, experimentation, and emergent strategy—and who are looking to upend traditional governance team models and create and remember anew.
Even with the perfect container, structure, and systems, it’s the people who make up our core team (our staff) and governance team – their own values as well as their willingness to be in the generative tension that helps support shared values – who have accelerated our work in shared power and leadership both on the core and governance teams. Together, we are living into our vision and deepening our practices of shared leadership and shared power to shift conditions towards love, dignity, and justice.
Look out for more learning from these experiments in liberatory governance in the new year!
Natalie Bamdad (she/her/hers), joined Change Elemental in 2017. She is a queer and first-gen Arab-Iranian Jew, whose people are from Basra and Tehran. She is a DC-based facilitator and rabble-rouser working to strengthen leadership, organizations, and movement networks working towards racial equity and liberation of people and planet.
Mark Leach (he/him/his) has over thirty years of experience as a researcher and management consultant. Mark has a particular interest in strategy, leadership development and transition, and issues of equity and inclusion in organizations.
Originally published at Change Elemental
Banner Photo Credit: Kirill Ignatyev | Flickr
The Art of Measuring Change
What are your associations with words such as “measurement”, “evaluation” or “indicator”? For many people these words sound annoying at best, and there are good reasons for it. Yet - given the fact that you clicked on this article - it’s also very likely that you are motivated to contribute to social change, and the main intention of this article is to share about the beauty and collaborative power of attempting to measure it. What I am not doing is offering quick solutions, the same way art is not a solution to a problem. Rather, it is an invitation to step back, look at the nuanced process of change with curiosity and an inquisitive mind, and maybe discover something new. The article is also available as a dynamical systems map.
In a nutshell
There are two ways of reading this article:
- Exploration mode: Use the systems map provided above and use the visual representation to navigate through the article more flexibly.
- Focussed mode: Stay here and follow the flow of the article.
Here already a quick overview of the main points and arguments:
- There is a good reason to be skeptical of impact measurement. If the approach taken is too simplistic and/or mainly serves to validate a perspective (e.g. of the donor), it’s almost impossible to measure what truly matters. Rather, such an approach further perpetuates existing power imbalances and puts beneficiaries at risk. (section: The dangers of linearity)
- The measurement of social phenomena has to pay justice to the intricacies and complexities of a project, a program, or any given action. This requires understanding, which puts empathy, listening and collaboration at the centre of an empowering approach to measuring change. (section: About potluck dinners and “power with”)
- Meaningful indicators serve as building blocks in the attempt to capture social change. An indicator is meaningful when it not only follows the SMART principles, but is also systemic and relevant, shared (understood and supported by all stakeholders) and inclusive (aware of power relationships). (section: Indicators that matter)
- Complexity science can provide an alternative scientific paradigm to understand and make sense of our world and, hence, to measure change. (section: Coming back to complexity)
- It’s time to equally distribute power, namely the ability to influence and shape “the rules of the game”, or potentially even the kind of game that is being played in the first place. A crucial step towards this is describing and defining what desired social change is and how we go about measuring it in a collaborative way. (section: Synthesis)
The starting point
I have been working in the field of impact evaluation and measuring social change for around 6 years now. I’ve interviewed cocoa farmers in Ghana, developed surveys and frameworks, crunched Excel tables of different sizes and qualities, mapped indicators, and held workshops on tracking change in networks. Doing all of this is way more than a job to me. I have met wonderful people on this path, have been part of impactful projects and really had the feeling of being able to contribute in a meaningful way.
To me, impact evaluation is an ambitious, creative and collaborative application of complexity science (more on that later). It can be a deeply empowering process that reveals hidden opportunities and structural challenges, creating empathy between groups of people.
And it can be harmful.
The dangers of linearity
Let me share a definition with you to explain what I mean:
“An impact evaluation analyses the (positive or negative, intended or unintended) impact of a project, programme, or policy on the target population, and quantifies how large that impact is.”*
I agree with that definition in general, yet when it comes to the details in language, my opinion differs significantly. For example:
- Nobody is or should be a target. We don’t shoot projects, programs or policies at people, we work with people.
- Quantification plays a role, but we should also qualify impact.
- It is not said who has the power to define “positive or negative”, and “intended or unintended”.
These are not simply trivial semantic differences. All too often I experienced situations where impact evaluation was used by organisations to prove and validate the effectiveness of their services, rather than to truly understand the perception and consequences of what they offer.
Here is an example of what I mean: A couple of years back I had the opportunity to visit cocoa farmers in Ghana for an impact evaluation for an NGO. We found out that, yes, the NGO’s activities are actually having an effect and are contributing positively to farmers’ income. But we did not capture in writing the fact that most farmers stopped growing subsistence crops for their own consumption, hence making themselves more vulnerable to global trends and market prices. A few months after I left, the market price for cocoa dropped significantly. We did not capture it as it was not part of our evaluation framework or our mental model about what counts as relevant information.*
This is what happens all too frequently: We have pre-defined and pre-conceived notions of what counts as a data point, and what doesn’t. This again is usually based on a linear model of thinking (aka “A” leads to “B”), not accounting for the complexities and intricacies of human interaction and social systems. I have talked to so many people in the field that were frustrated, stating something along the lines of “we don’t measure what is truly relevant”.
To put it another way: If empathy and understanding are not at the centre of impact evaluation, both as the foundation and the goal, then it might be (unintentionally!) used against the people we want to benefit. It’s like having a knife in your hand. You can use it to prepare a delicious meal, but also to hurt yourself and others.
About potluck dinners and “power with”
Let’s dig a bit deeper into that: We’ve learned that what we do in impact evaluation is to assess the change attributed to an intervention (a project, program, workshop etc.). You do something and then something else happens. Now, we want to understand the “somethings” and how they are connected. This is not as simple a task as it may seem. Reasons include:
- We humans love to make our own meaning. You (and your organisation) probably know what the intervention is, but others perceive it fromtheir own perspective and life reality.
- Change is like air: Ever-present and hard to grasp. The “mechanics” of change can’t be pinned down easily and require us to look at context & conditions. Similarly, we know how difficult predictions are. Should we trust the weather forecast? For the next 3 to 5 days probably, but beyond that?
- There is power in the game: Oftentimes, multiple stakeholders and their multiple opinions are involved in an evaluation. There is nothing wrong with that per se, yet it is important to acknowledge.
The art of impact evaluation, therefore, is not to publish fancy reports, but to apply it in such a way that it deepens the internal understanding of issues at hand and strengthens the collaboration between actors. When this is the case, It builds empathy and human connection, and enables stakeholders to jointly develop shared meaning and scenarios for social change and transformation.
In other words, impact evaluation is based on and deepens listening. Listening not only to people, but to their context and to groups of people, to underlying and invisible challenges and hopes.*
In a more recent project I worked on we called all stakeholders together from the very beginning. It was clear who “has the money”, but we also shared the ambition to collaborate on a level playing field. As a consequence, we co-developed the project’s vision and the evaluation framework. We made clear that the first round of data collection also serves the purpose to understand what is relevant; and that the project goals will be further developed based on the “reality on the ground” rather than the content of the funders’ strategy paper.
We created the space for a genuine dialogue, and the data collected further strengthened the mutual understanding and trust in the group and in the process. It revealed both further challenges and where the leverage points are for creating systemic impact. It also became clear that power is not only linked to money.
“What makes power dangerous is how it’s used. Power over is driven by fear. Daring and transformative leaders share power with, empower people to, and inspire people to develop power within.” (Brené Brown)*
What we did was to ask a different question than normal. The central question was not “how can one central stakeholder prove their impact?”, but rather “how can we jointly contribute to desired change for a matter that we all care about?”. Shifting the question means that stakeholders and their individual contributions are valued differently, and that the quality of interaction changes.
Speaking in the metaphor of our delicious meal: We did not go into a restaurant where you tell somebody what should be cooked for you. Rather, we sent out the invitation to join a potluck dinner. Organising a dinner in this way does not happen at random. It requires clarity on roles and contributions, as well as shared agreements (e.g. on when and where to meet). The fundamental difference to a restaurant visit, though, is that it values participation and what each stakeholder (dinner guest) brings to the table, which in turn requires a mindset of being curious and open to surprises.
So far so good, but how do we actually measure change?
Jannik Kaiser is co-founder of Unity Effect, where he is leading the area of Systemic Impact. His desire to co-create systemic social change led him down the rabbit holes of complexity science, human sense-making (e.g. phenomenology), asking big questions (just ask “why” often enough…) and personal healing. Having worked in the NGO sector, academia and now social entrepreneurship
Originally published at Unity Effect
featured photo by Adi Goldstein on Unsplash
The illusion of hopelessness
The war in Ukraine is a symptom of something bigger— and within reach
In times of war, we are led to believe we are powerless.
We are told that violence is inevitable, an unfortunate part of the way things are. And that the way things are cannot change.
As world events have transpired over the last two weeks, this illusion has begun to splinter
* * *
Russian military forces invaded a sovereign nation on February 24th. Within days, the United States, the European Union, and other nations announced a series of economic sanctions on Russia. At the same time, countries of the European Union waived visa rules for Ukrainian refugees–allowing those fleeing war to enter the EU without having to seek asylum.
Homes across Europe have opened their doors to Ukrainians fleeing war, and President Biden announced that Ukrainian refugees would be welcome in the US “with open arms.”
These moves were swift and unprecedented. Rules that had long existed were replaced with new ones. Systems changed as people and countries moved together in response to a humanitarian crisis.
How quickly rules can change when we want them to.
How malleable systems can be when we agree on what is right.
* * *
Russia’s attack on Ukraine, like all wars, is a symptom of a worldview of domination and extraction.
Like all wars, it exists amid other symptoms and consequences of this worldview: modern dependence on oil and the interests of the fossil fuel industry; unmistakable racism at the Ukrainian border as Africans were systematically turned away.
And the global coordination to condemn Russia’s attack and support the Ukrainian people was made possible, in part, by white supremacy: Western sensibilities were stirred by seeing white refugees. Meanwhile, escalating humanitarian crises in Afghanistan, Palestine, Yemen, Syria, Somalia, and Ethiopia have not been met with the same swiftness.
Imagine a world where all people in need were met with dignity and humanity. Where violence and harm was met with resounding care.
Imagine systems of governance that hold these values above all others.
* * *
In times of war, we are led to believe we are powerless by those who benefit from our silence. We are led to believe our collective systems cannot change by those who benefit from the way things are. Meanwhile, worldviews of domination and extraction continue to shape our reality and perpetuate harm.
As the war in Ukraine has unfolded, we’ve also seen a wave of dehumanizing legislation against queer and trans young people, increasing threats to reproductive justice, and an alarming epidemic of homelessness continuing in the US, all while COVID cases spike in Europe and Asia.
When we understand that all violence is a symptom with the same cause, we can also see that we are not just spectators to what is happening — in Ukraine or right beside us.
There is hope, and the hope is us.
* * *
“There is never time in the future in which we will work out our salvation.
The challenge is in the moment; the time is always now.”
~James Baldwin
Resonance Network is a national network of people building a world beyond violence.
Originally published 3.16.22 at Reverb
Seeing the World Through a Network Lens
June Holley offers Network Weaving Workshop, another training slide deck for use in your organization or network. It provides an introduction to many network concepts and includes a number of activities such as speed networking, mapping your network, and the Network Weaver Checklist.
This slide deck is particularly good for sets of organizations who are not well connected. As result of this session, they would be starting to see the world through a network lens.
The slides are offered in pdf format, but we are also sharing a link to the google slides. Create a copy of the presentation and save it as a new name in your google drive. This way, you can modify them to adapt the presentation to the particular group you are working with.
Access the Network Weaving Workshop slide deck HERE.
June Holley has been weaving networks, helping others weave networks and writing about networks for over 40 years. She is currently increasing her capacity to capture learning and innovations from the field and sharing what she discovers through blog posts, occasional virtual sessions and a forthcoming book.
featured image found HERE
THE TAPESTRY: Weaving Life Stories
You are invited to listen to The Tapestry Podcast.

The podcast is about bringing people together to explore the rich, woven textures of our narratives. Our stories are impactful and in listening to the stories of others, we learn more about our own power, claim our purpose and pursue our passion. The fabric of our lives as women is strong, resilient and when we come together, we can make a beautiful piece of work to inspire, support and sustain our personal and professional lives. Although designed for women 50 and above, the wisdom shared is ageless. Join us as we share, laugh hysterically, cry, and keep it real all at the same time.
Some of The Tapestry's most recent episodes include:

THE STORIES BEHIND THE DATA - Meme Styles
In 2015, Meme Styles founded MEASURE to promote the use of evidence-based projects and tools to tell real-life stories behind the numbers. As a catalyst for systems change, MEASURE has grown to a fully operational nonprofit social enterprise that provides free data support to Powerful Black and Brown-led communities. So far the organization has provided over 3000 free data support hours to Black and Brown - led organizations.

CREATING A PERSONAL NETWORK FOR TRANSFORMATION -- June Holley
June Holley has been weaving networks - and helping other learn to weave networks – for over 40 years. Much that she learned is included in The Network Weaver Handbook, 400 pages of simple activities and resources for Network Weavers. She also created www.dev.networkweaver.com, a site with many free resources and a blog authored by over 40 network weavers.

BOUNDARIES IN BUSINESS AND IN LIFE FOR 2022 - Kimberly Oneil
Kimberly O'Neil is an award-winning professor, executive leader, and social good expert. She was the youngest serving African American woman City Manager in the United States. As a veteran senior government and nonprofit executive, Kimberly has used her voice to impact policy decisions while lobbying in New York City and on Capitol Hill. She now works within the social sector and leads Giving Blueprint, a consulting company with a mission to impact social change through the development of strategic partnerships and growth plans within the social sector.

CRITICAL CONVERSATIONS ABOUT RACE - Amber Sims
Amber currently serves as the Executive Director of Young Leaders Strong City, a nonprofit focused on youth development, leadership, and racial equity. She was formerly the Director of Regional Impact for Leadership for Educational Equity, an educational nonprofit focused on leadership pathways in civic engagement. Previously, Amber led workforce development at Workforce Solutions Greater Dallas Opportunity Center. Her theory of change was to emphasize the connection between education, workforce, and dual generation impact.
Other guests have included:
- Dallas Maverick CEO and President Cynt Marshall
- Leah Frazier , 2-Time Emmy Award-Winning and 10-Time ADDY Award-Winning entrepreneur
- Paula Stone Williams, internationally known speaker on issues of gender equity, LGBTQ advocacy, and religious tolerance
- Rafia Zakaria, author of Against White Feminism (W.W. Norton, 2021) and Veil (Bloomsbury, 2017) and a writer for the Guardian, Boston Review, The New Republic, The New York Times Book Review and Al Jazeera America
- Gretchen Bauer, Luxury handbag manufacturer
Find all The Tapestry episodes HERE

Dr. Froswa’ Booker-Drew is a Partnership Broker. Relational Leadership Junkie. Connector. Author/Speaker/Trainer. Co-Founder, HERitage Giving Circle. Currently, the Vice President of Community Affairs of the State Fair of Texas, she has been quoted and profiled in Forbes, Ozy, Bustle, Huffington Post and other media outlets around the world. In addition, she has been asked to speak on a variety of topics such as social capital and networking, leadership, diversity, and community development to national and international audiences. This included serving as a workshop presenter at the United Nations in 2013 on the Access to Power.
featured image found HERE

Network Weaver is dedicated to offering free content to all – in support of equity, justice and transformation for all.
We appreciate your support!
donate in the box above or click here
Businesses without Bosses: from hard-nosed leadership to sustainable, self-managing systems
As many of you know, I’m very passionate about helping people understand and experiment with self-organizing.
Joella Bruckshaw and Julian Saipe are executive coaches who have a wonderful podcast series called ‘Behind The Screen’ where they share leadership insights with high profile leaders. In this series of impromptu discussions, Joella and Julian, along with their invited guests, discuss success, the characteristics we choose to reveal, and those we choose to keep behind the screen - engaging thoughts on leadership, performance, authenticity and having fun.
In Episode 12 of the podcast series, Joella and Julian talked with me about Self-Organization.
Our conversation explored how “businesses without bosses” can thrive, just as nature’s own eco-systems do. We also discussed how coaching could facilitate a transition from hard-nosed leadership to sustainable, self-managing systems, where purposefulness itself is the outcome.
Access the interview on Behind the Screen podcast at: iTunes/Apple HERE & Amazon Music HERE
June Holley has been weaving networks, helping others weave networks and writing about networks for over 40 years. She is currently increasing her capacity to capture learning and innovations from the field and sharing what she discovers through blog posts, occasional virtual sessions and a forthcoming book.
featured image found HERE